Alkaline Herbal Benefits, Deficiency and Excess Effects
Alkaline refers to a property related to the pH level of a substance. Alkaline foods and their impact on the body have been a topic of interest in health and wellness circles
-
- Alkaline describes something that is basic or has the properties of an alkali.
- Alkalis are substances that can neutralize acids and have a pH greater than 7.
- Alkaline substances are often found in nature, such as in certain minerals, soils, and water sources.
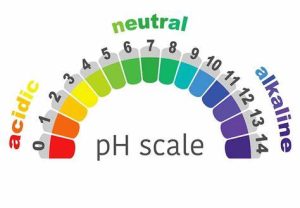
- The pH scale measures how acidic or alkaline a substance is.
- It ranges from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very alkaline).
- A pH of 7 is considered neutral (neither acidic nor alkaline).
- Alkaline substances have a pH greater than 7.
- Alkaline Water:
- Alkaline water is slightly less acidic than regular tap water.
- It contains alkaline minerals such as calcium, potassium, magnesium, or iron.
- Some people believe that drinking alkaline water offers health benefits, but research supporting these claims is limited.
Remember that maintaining a balanced pH level in your body is essential for overall health. While alkaline water may have some potential benefits, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes
What does Alkaline do in the Human body?
Alkaline foods and their impact on the body have been a topic of interest in health and wellness circles. While the scientific evidence is not always conclusive, here are some potential effects of consuming alkaline foods:
- Balancing pH Levels: Alkaline foods are believed to help maintain a more balanced pH level in the body. Our body’s pH scale ranges from acidic (0) to alkaline (14), with 7 being neutral. Some proponents of the alkaline diet argue that consuming more alkaline foods can counteract the acidity caused by certain foods and metabolic processes.
- Bone Health: Alkaline foods may support bone health. The theory is that an acidic environment can lead to calcium loss from bones. By consuming alkaline foods, you can help prevent this calcium loss and maintain stronger bones.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Some alkaline foods, especially fruits and vegetables, are rich in antioxidants and phytonutrients. These compounds have anti-inflammatory effects and may contribute to overall health.
- Digestive Health: Alkaline foods are often high in fibre, which supports healthy digestion. They can also help regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation.
- Energy Levels: Advocates of the alkaline diet claim that it can boost energy levels. However, this effect is likely due to the overall health benefits of consuming nutrient-rich foods rather than the alkalinity itself.
- Weight Management: Alkaline foods are typically low in calories and high in nutrients. Including them in your diet can promote weight loss and overall well-being.
Keep in mind:
- The body has its mechanisms to regulate pH levels, and it is not solely dependent on dietary choices.
- The alkaline diet is controversial, and scientific evidence supporting its benefits is limited.
- A balanced diet that includes a variety of foods (both acidic and alkaline) is essential for overall health.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific needs and health conditions.
Low alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels
Certainly! Low alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels can be a sign of various underlying conditions. Let’s explore this further:
- What Is Alkaline Phosphatase?
- Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme found in the blood that plays several essential roles in the body.
- It is produced mainly by the liver and bones, with smaller quantities synthesized by the intestines and kidneys.
- ALP contributes to processes such as:
- Transporting nutrients and enzymes to and from the liver.
- Aiding in bone development, growth, and maintenance.
- Facilitating the transport of calcium and phosphate from the intestines to bones, muscles, and nerve cells.
- Assisting in the transport of fatty acids for energy storage and maintaining cell integrity.
- Regulating cell growth during pregnancy.
- Causes of Low Alkaline Phosphatase:
- Abnormally low ALP values may result from various conditions:
- Achondroplasia: A form of dwarfism.
- Aplastic anaemia: Anemia caused by bone marrow failure.
- Celiac disease: An autoimmune disease triggered by gluten.
- Congenital iodine deficiency: Affects bone growth.
- Hypophosphatasia: A congenital disorder affecting bone development.
- Hypothyroidism: Low thyroid function.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
- Malnutrition: Insufficient intake of essential nutrients.
- Pernicious anaemia: An autoimmune form of anaemia.
- Abnormally low ALP values may result from various conditions:
- Symptoms and Treatment:
- Symptoms related to low ALP levels may not always be apparent, but they can include bone or joint pain.
- Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
- Nutritional Improvement: Ensuring sufficient protein and carbohydrate intake.
- Addressing specific conditions (e.g., thyroid disease, celiac disease) as needed.
- Consultation with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Remember that low alkaline phosphatase levels are less common than high levels, but they can still have significant implications. If you suspect any health issues related to ALP, consider seeking medical advice for proper evaluation and management.
Excess alkalinity in the body (Alkalosis)
Excess alkalinity in the body, also known as alkalosis, can have several negative effects. Let’s explore these in more detail:
- Metabolic Alkalosis:
- Definition: Metabolic alkalosis occurs when your blood becomes overly alkaline due to an imbalance in acid-base levels.
- Causes:
- Loss of Acid: It can result from excessive vomiting, leading to a loss of stomach acid.
- Excessive Bicarbonate: Overuse of antacids or accidental ingestion of bicarbonate (found in baking soda) can increase blood bicarbonate levels.
- Potassium Depletion: A large loss of potassium or sodium in a short time can contribute to metabolic alkalosis.
- Symptoms:
- Early symptoms may include nausea, numbness, prolonged muscle spasms, and hand tremors.
- Severe symptoms can lead to confusion, stupor, coma, and difficulty breathing.
- Treatment:
- Mild cases may require dietary adjustments (e.g., increasing salt intake).
- Immediate treatment involves intravenous saline solution (sodium chloride) to restore balance.
- Addressing underlying causes is crucial.
- Respiratory Alkalosis:
- Cause: Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there’s insufficient carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the bloodstream due to rapid, uncontrollable breathing (hyperventilation).
- Symptoms: Early symptoms include dizziness and muscle twitching.
- Treatment:
- Address the underlying cause (e.g., pain management).
- Supplemental oxygen and therapies to reduce hyperventilation risk are essential.
- Hypochloremic Alkalosis:
- Cause: Significant decline in chloride due to prolonged vomiting or sweating.
- Importance of Chloride: Chloride is crucial for maintaining balance in bodily fluids and digestive processes.
- Treatment: Address the underlying cause and restore chloride levels.
- Hypokalemic Alkalosis:
- Cause: Insufficient potassium (hypokalemia) disrupts the acid-base balance.
- Importance of Potassium: Potassium is essential for heart, kidney, muscle, nervous system, and digestive function.
- Treatment: Address potassium deficiency (e.g., through diet or supplements).
Remember that severe alkalosis can lead to shock or coma, so seeking medical attention promptly is crucial if you experience severe symptoms.
Alkaline herbs
Alkaline herbs offer a natural way to promote overall health by helping balance the body’s pH levels. These herbs are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. Let’s explore some of these beneficial alkaline herbs:
- Lemon Balm (Melissa officinalis):
- pH: Around 7.5.
- Benefits: Known for its calming properties, lemon balm aids in stress relief and supports better sleep.
- Burdock Root (Arctium lappa):
- pH: Approximately 7.3.
- Benefits: Traditionally used for detoxification, burdock root supports liver function, purifies the blood, and contributes to clear, radiant skin.
- Chlorella (Chlorella vulgaris):
- pH: About 8.0.
- Benefits: This green algae is a potent source of nutrients, including chlorophyll, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It bolsters overall health and vitality.
- Sea Moss (Chondrus crispus):
- pH: Ranges from 8.0 to 9.0.
- Benefits: Packed with essential minerals, sea moss promotes a healthy thyroid, improved digestion, and enhanced immune function.
- Peppermint (Mentha × Piperita):
- pH: Approximately 7.0.
- Benefits: Revered for its soothing properties on the digestive system, peppermint leaves can help alleviate indigestion, bloating, and discomfort.
- Red Clover (Trifolium pratense):
- Benefits: Often used to support detoxification, red clover’s alkaline properties contribute to maintaining an optimal pH level.
- Nettle (Urtica dioica):
- Benefits: A nutrient-rich herb with alkalizing benefits, nettle is commonly consumed as a tea or in supplement form to support overall health.
Remember to incorporate these alkaline herbs into your diet mindfully, and consult with a healthcare professional if you have specific health concerns.
External links
alkaline deficiency in the body
herbal benefits of alkaline




Review Alkaline.
You must be logged in to post a review.